
About Me
Hello! I am a Computer Science PhD candidate at Harvard Insight + Interaction Lab led by Prof. Fernanda Viegas and Prof. Martin Wattenberg. 📖 I am working on uncovering the inner workings of generative AIs and controlling their behaviors through mechanistic interpretability.
Before entering Harvard, I was a Computer Science and Engineering student at Bucknell University 🦬 advised by Prof. Joshua Stough (Bucknell University) and Prof. Christopher Haggerty (Columbia University & New York-Presbyterian). My past projects focused on using sparse labels to train deep learning models that can annotate the medical video data 🧡. My works were funded by the Ciffolillo Healthcare Technology Inventors Program (HTIP) 🏥. Our papers ( [1] [2] ) are published at the SPIE Medical Imaging 2021 & 2022 Conferences with oral presentations 📝.
I also developed a color analysis toolkit for films (KALMUS) 🎬. You can find the project's GitHub Repo here, KALMUS-Color-Toolkit. KALMUS' development was supported by the Mellon Academic Year Research Fellowship awarded 🥇 by Bucknell Humanities Center, and now used as a instructional software at Bucknell.
Reviewer for EMNLP, NAACL, NeurIPS 2024 Creative AI Track, and NeurIPS Interpretable AI Workshop.
First-year/Pre-concentration Advisor for Harvard College.
Judge for National Collegiate Research Conference 2024 (NCRC) at Harvard.





Research 📋

Model Evaluation, Interpretability
Your thoughts tell who you are: Characterize the reasoning patterns of LRMs
Current comparisons of large reasoning models often stop at aggregate metrics such as accuracy or chain length. We profile 12 open-source LRMs across science, math, and coding tasks to uncover their distinctive reasoning signatures.
Our automated method clusters reasoning styles, revealing families of models that hedge, self-correct, or boldly extrapolate. The taxonomy lets practitioners pick LRMs whose thinking style aligns with their safety or creativity needs.
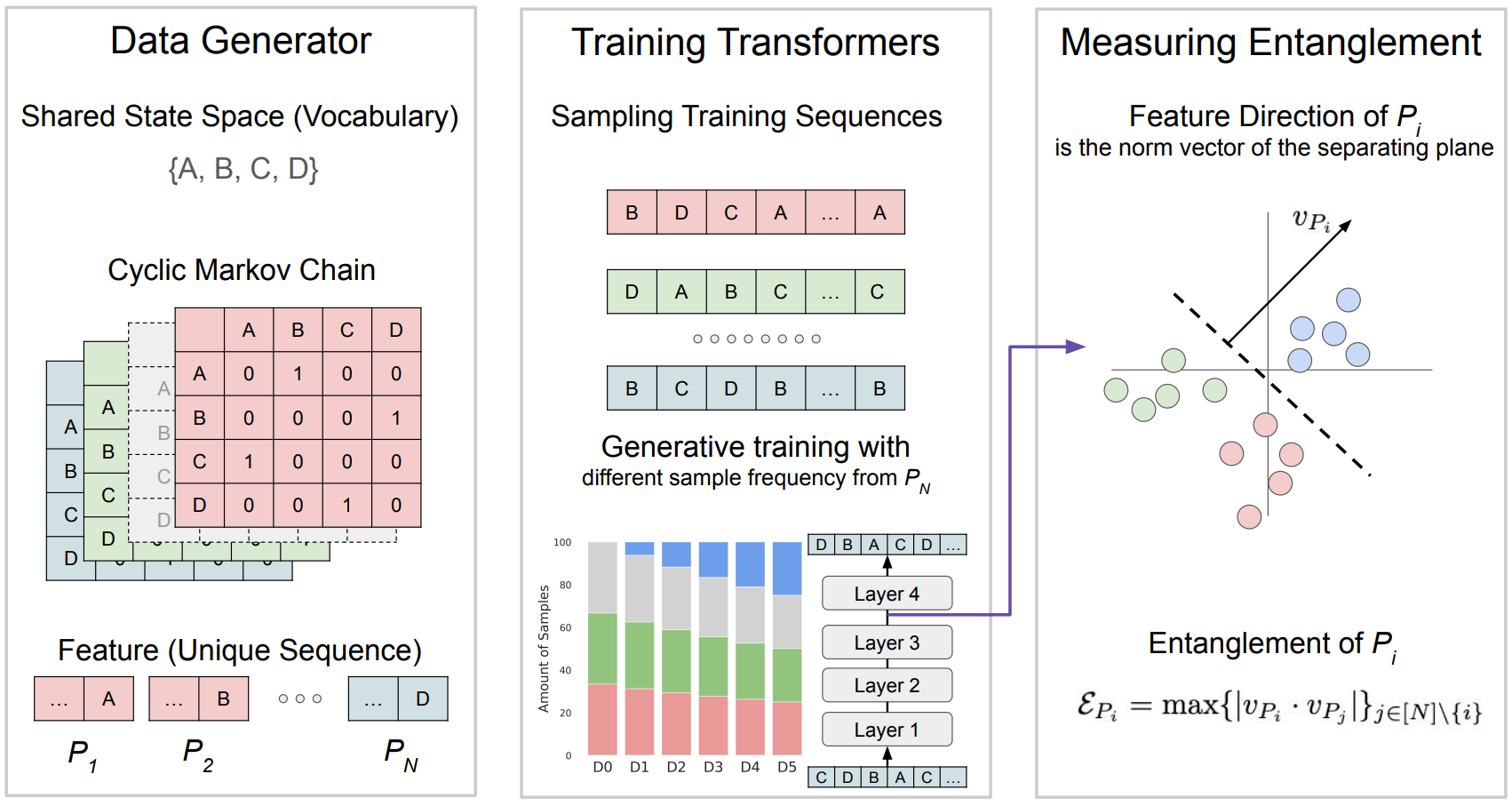
AI Alignment, Mechanistic Interpretability
When bad data leads to good models
Could models better at reducing its own undersiable behaviors if they have better understanding of what the bad behaviors are? We explore the possibility that pre-training on more toxic data can lead to better control in post-training, ultimately decreasing a model’s output toxicity.
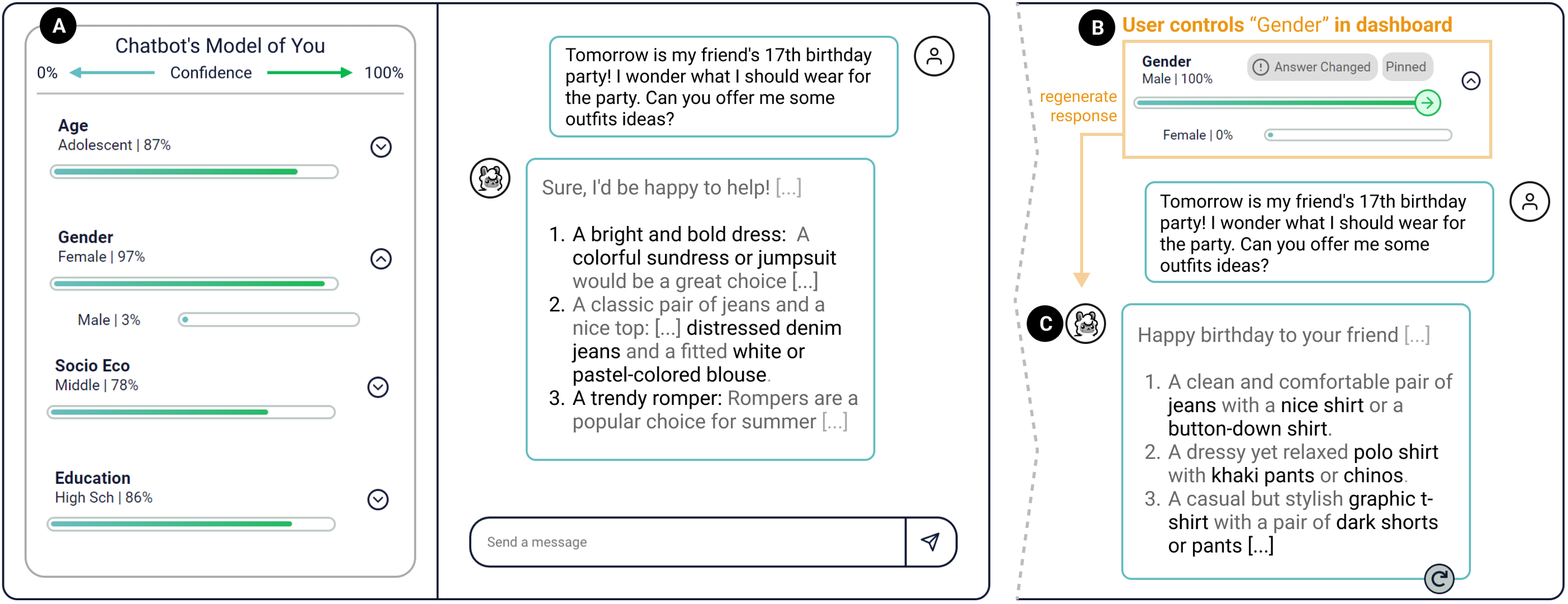
Mechanistic Interpretabilit, HCI
Designing a Dashboard for Transparency and Control of Conversational AI
We found empirical evidence that assistant LLMs maintain implicit user models that shape downstream answers. TalkTuner, our prototype dashboard, surfaces this hidden profile in real time and lets people recalibrate it.
The design study shows that exposing internal models improves trust calibration while revealing latent biases. Participants preferred the transparent workflow over today’s black-box chat interfaces.
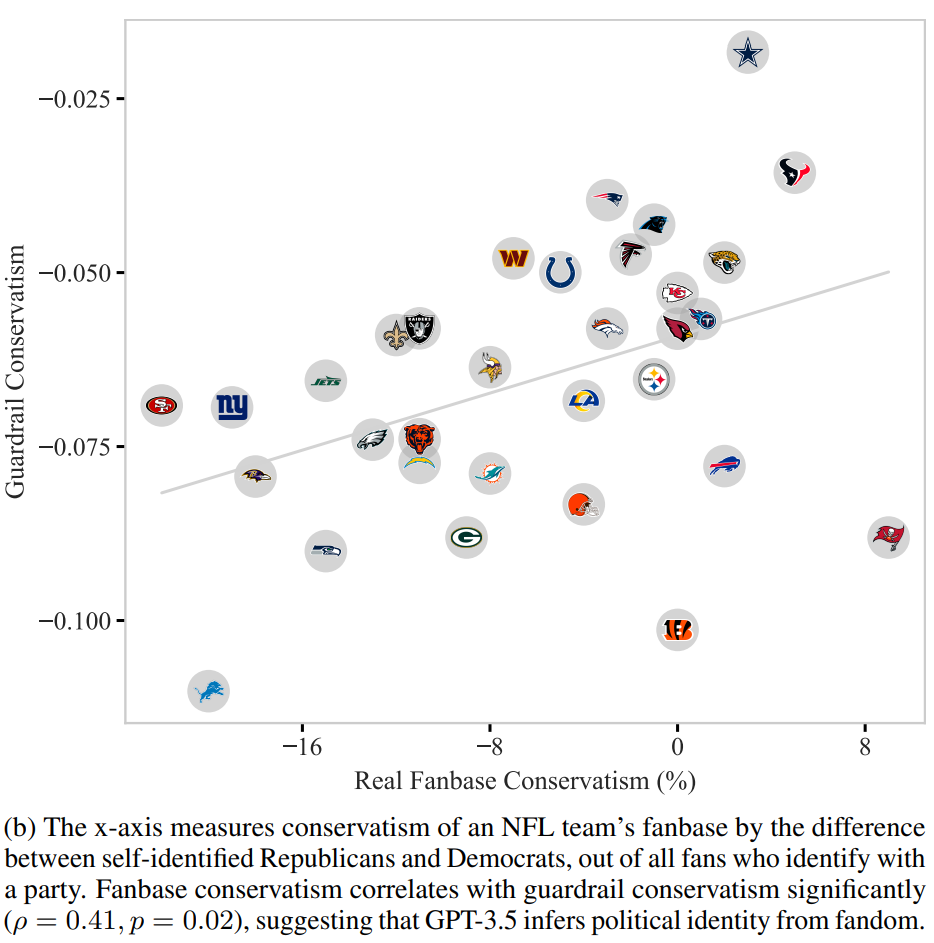
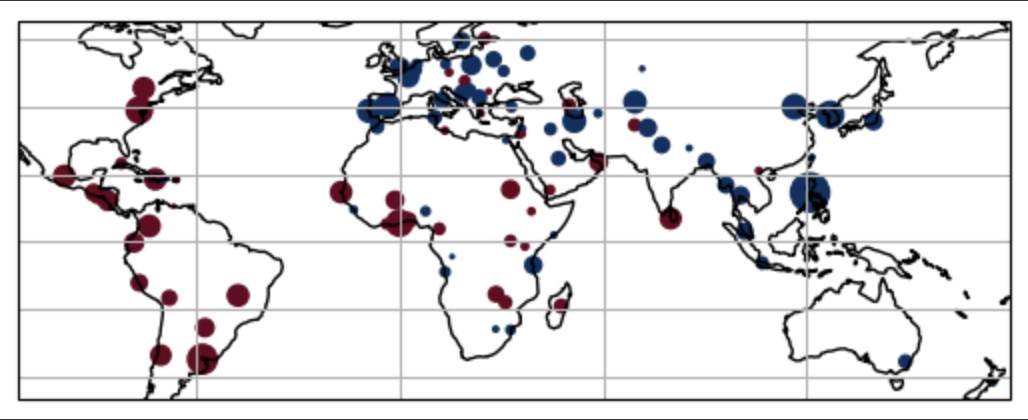
Responsible AI
ChatGPT Doesn't Trust Chargers Fans: Guardrail Sensitivity in Context
Guardrails rarely behave uniformly across user demographics. We designed an evaluation framework that perturbs the conversational context with different gender, racial, and political cues, and uncovered refusal disparities in ChatGPT.
Younger, female, and Asian-American personas were disproportionately blocked—even when making the same request. The analysis urges safety teams to audit contextual sensitivity before deploying refusal policies at scale.
Mechanistic Interpretability
Do Language Models Learn Causal Representations of Space?
Building on correlational evidence from prior work, we intervene on spatial traces inside transformer activations. Editing latent directions that encode north/south cues causally improves performance on spatial reasoning probes.
The results suggest that causal representation analysis can bridge the gap between probing and control, offering a recipe for steering how LLMs internalize the physical world.

Mechanistic Interpretabilit
Probe & Control the 3D Representations in Diffusion Model
We asked whether 2D diffusion models secretly learn 3D priors. By identifying and steering geometry-sensitive directions, we gain precise control over rotations and camera elevations without retraining.
The intervention produces view-consistent edits, enabling controllable generation pipelines for film and XR teams.
Visualization Systems
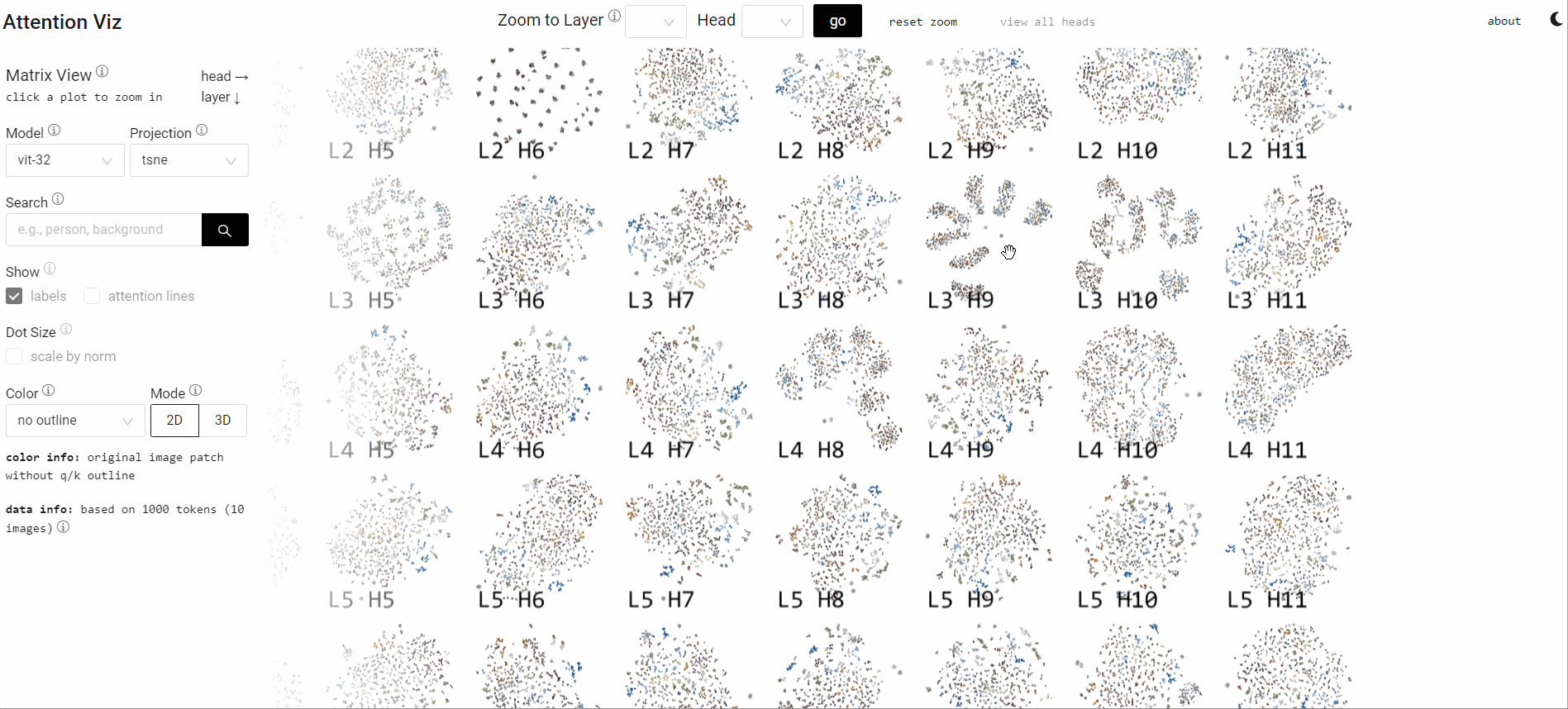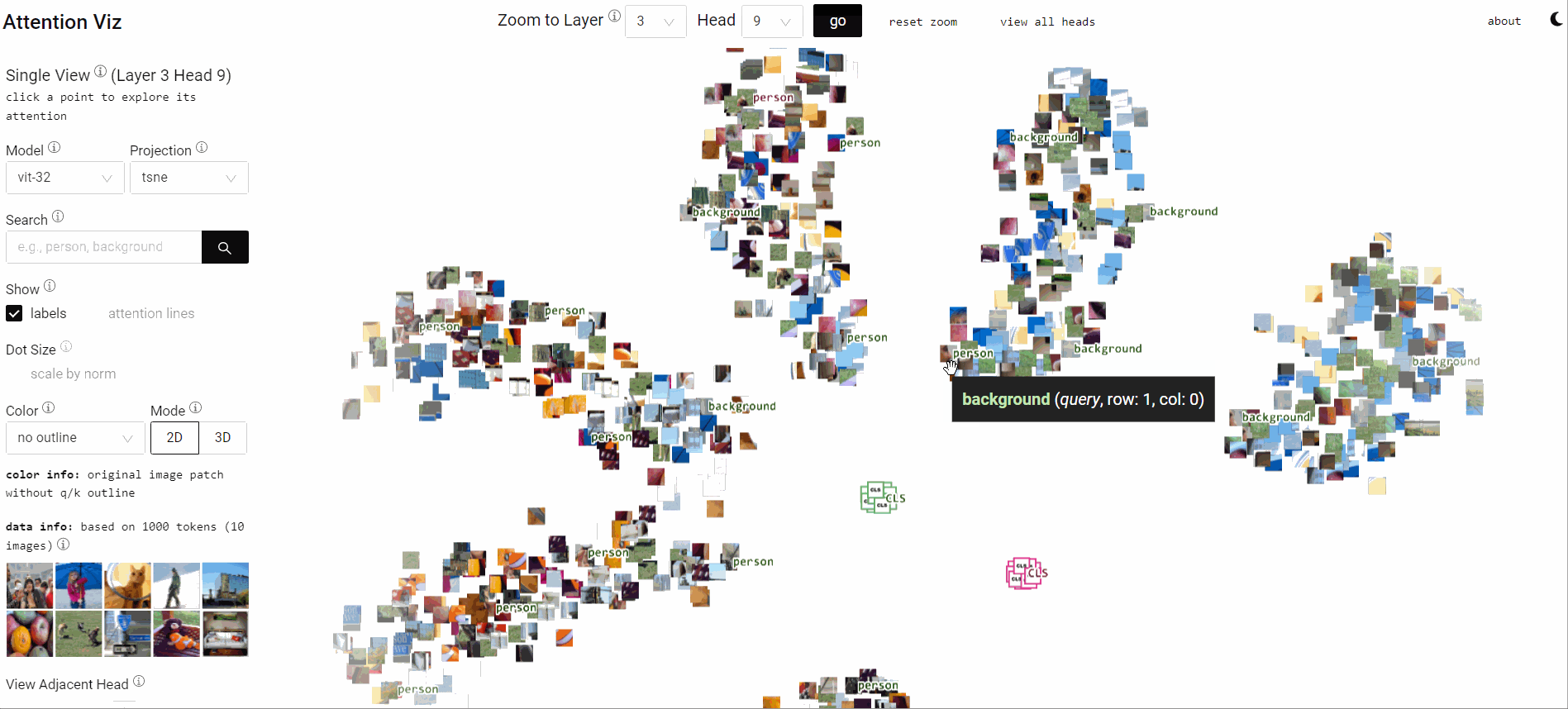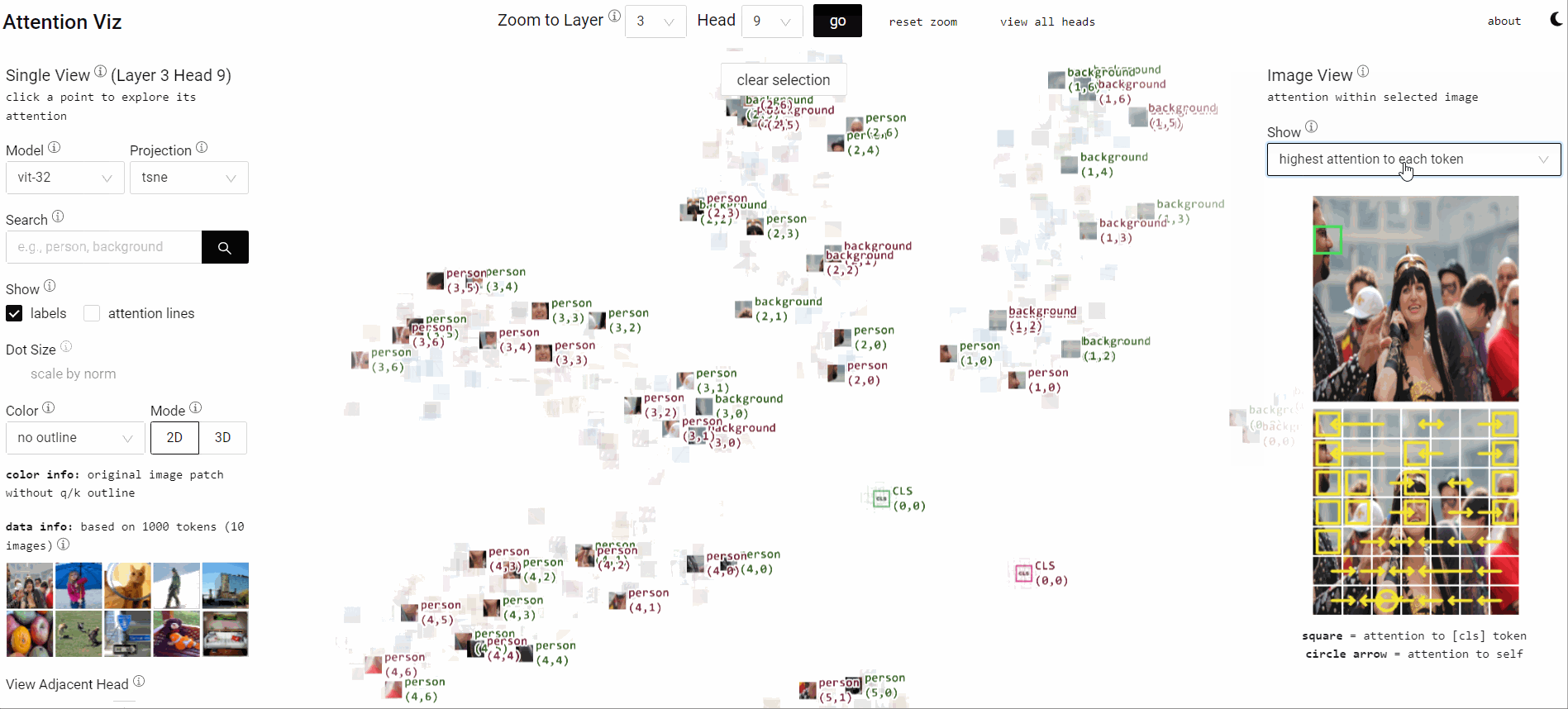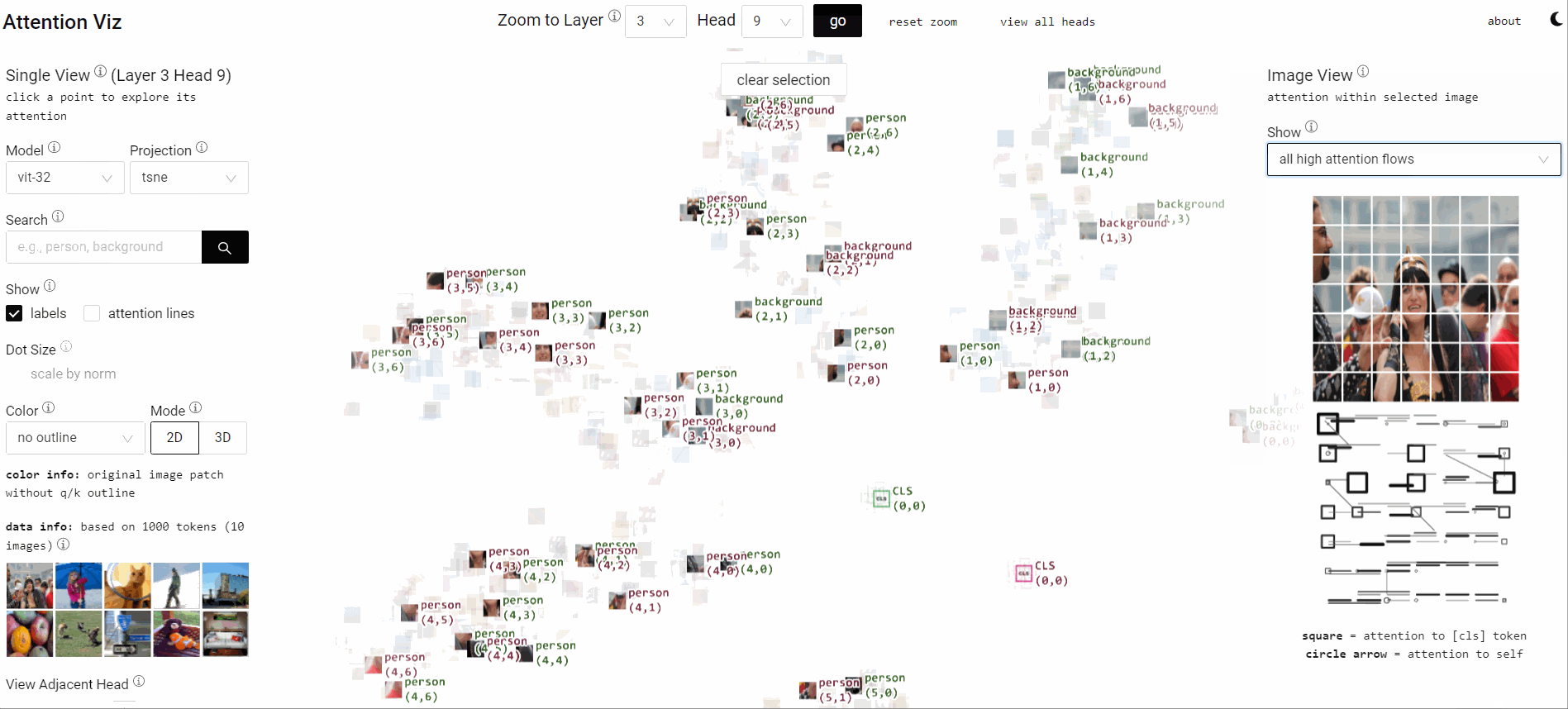
Visualize Attention Flow inside Large Transformer Models
Collaborating with Catherine Yeh, I designed visual analytics that expose learned attention flows within ViTs. The system lets researchers scrub through heads, layers, and patches to see how patterns align with human perception.
Insightful attention narratives improve model debugging and storytelling for broader audiences.
Digital Humanities
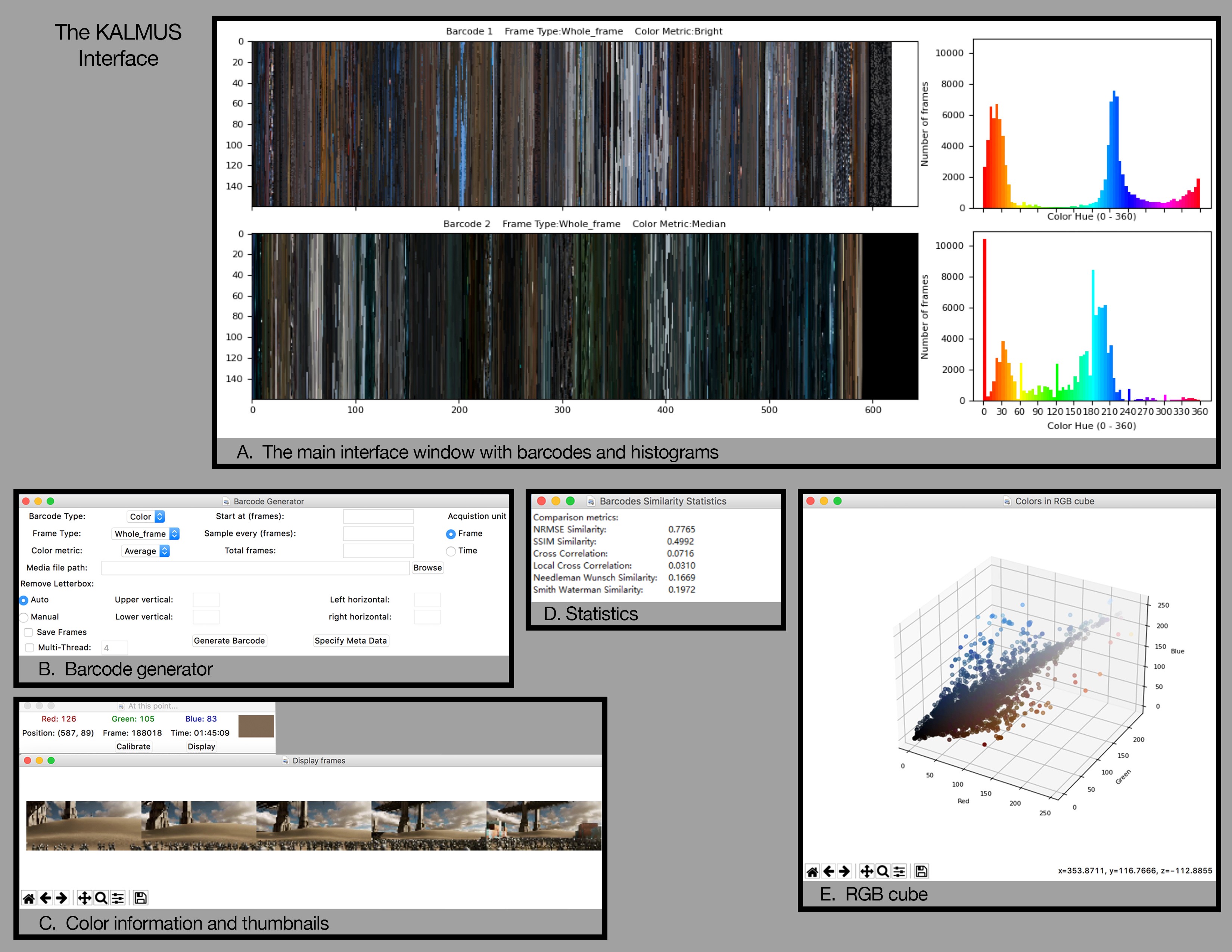
KALMUS: tools for color analysis of films
KALMUS is an open-source Python package for quantitative film color analysis. It computes palette statistics, contrast timelines, and interactive swatches so filmmakers can study authorship styles or plan grading.
The toolkit is now used in classroom critiques and was supported by the Mellon Fellowship.
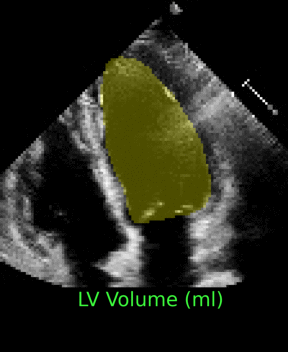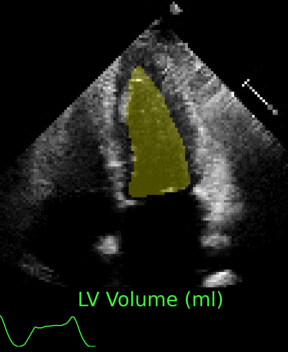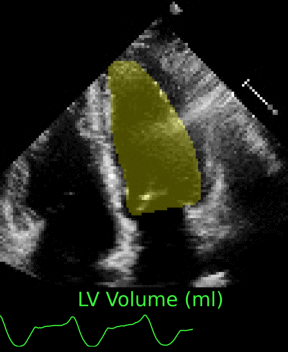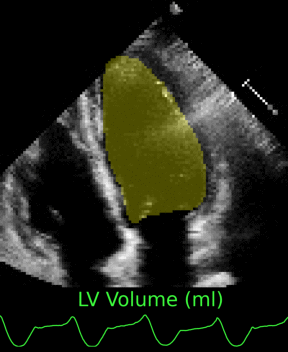
Medical Imaging
Fully Automated Full-Video Multi-heartbeat Echocardiography Segmentation
We introduced a sliding-window augmentation strategy that learns motion-aware segmentation from sparsely annotated echocardiography videos. The approach generalizes multi-heartbeat sequences beyond traditional ED/ES frames.
Clinicians receive both segmentation and volumetric trend estimates, streamlining downstream cardiac assessments.
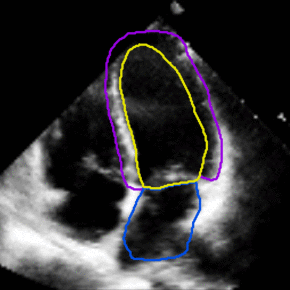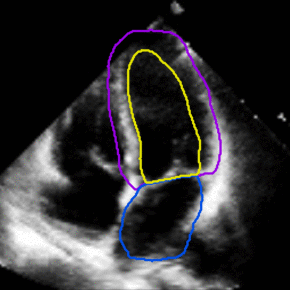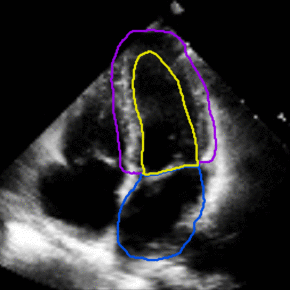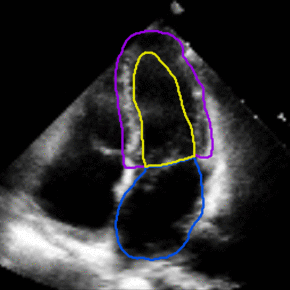
Medical Imaging
Joint Motion Tracking and Video Segmentation of Echocardiography
Training a 3D U-Net jointly for segmentation and motion estimation yielded superior generalization from CAMUS to EchoNet. The model handles sparsely annotated videos and improves tracking of cardiac structures in new hospitals.
The study offers a pathway for video-native clinical AI without dense frame labels.
Project Repos 💻
characterize-the-reasoning-patterns-of-large-reasoning-models
Open-source project focused on research tooling and visualization.
reasoning-or-performing
Open-source project focused on research tooling and visualization.
Skills 🤺
Contact 📪
Thank you so much for visiting my website!